- Код статьи
- S020595920024908-4-1
- DOI
- 10.31857/S020595920024908-4
- Тип публикации
- Статья
- Статус публикации
- Опубликовано
- Авторы
- Том/ Выпуск
- Том 44 / № 2
- Страницы
- 63-74
- Аннотация
Одними из особенностей работы головного мозга людей, страдающих шизофренией, являются изменения активности их мозга при зрительной категоризации одушевленных и неодушевленных объектов. Целью данного исследования был анализ мозговой активности людей, страдающих шизофренией, в ходе зрительной категоризации ими объектов, имеющих различные семантические и физические характеристики. Предполагалось, что паттерны мозговой активности на ранних и поздних этапах зрительной обработки различаются у людей, страдающих шизофренией, и людей из нормативной выборки. С помощью метода зрительных вызванных потенциалов изучали особенности активности головного мозга у 25 людей, страдающих шизофренией от 1 года до 7 лет, при категоризации ими изображений живой и неживой природы, низкой и высокой пространственной частоты. Было выявлено, что амплитуды P170 (N170) в левом и правом задневисочных и центральном отведениях, а также амплитуды P300 в центральном отведении у людей с шизофренией не отличаются при категоризации одушевлённых и неодушевленных объектов. Такие особенности работы мозга не характерны для людей из нормативной выборки. Выявленный результат важен для лучшего понимания перестройки работы мозга при зрительном восприятии объектов разных категорий, возникающей при развитии шизофрении.
- Ключевые слова
- шизофрения, когнитивные зрительные потенциалы, высокая и низкая частота, объекты живой и неживой природы, категоризация объектов
- Дата публикации
- 29.03.2023
- Год выхода
- 2023
- Всего подписок
- 13
- Всего просмотров
- 404
Одним из самых важных в когнитивной нейропсихологии по-прежнему остается вопрос, каким образом мозг преобразует перцептивную информацию в осмысленные понятия и категории [10; 11; 14; 16; 18]. Новые методы нейровизуализации и обработки данных позволяют глубже изучить процесс перестройки нейронных процессов, лежащих в основе распознавания объектов.
Ряд исследований зрительной системы человека рассматривают такую характеристику как одушевленность (различение объектов живой и неживой природы) в качестве ключевого принципа организации репрезентаций об объектах. Это свойство имеет первостепенное значение для нашего понимания зрительного мира, обеспечивая базовое упорядочение нашего восприятия [16; 18–20].
Согласно результатам исследований, полученным методами функциональной магнитно-резонансной томографии [18], магнитоэнцефалографии и электроэнцефалографии [13; 16; 18], при категоризации одушевленных объектов возникают паттерны активации мозга человека, отличные от тех, которые наблюдаются при категоризации неодушевленных объектов. Декодирование данных временных рядов с использованием магнитоэнцефалографии и электроэнцефалографии дало возможность исследовать временные рамки формирования репрезентаций объектов в головном мозге человека, раскрывая динамическую эволюцию структуры категорий объектов с течением времени [16]. Результаты исследования магнитоэнцефалографии и электроэнцефалографии при применении немного отличающихся визуальных задач и объектов показали, что начало и пик декодирования одушевленности объектов возникают между 66 и 157 мс или от 80 мс до 240 мс [13] после предъявления объекта. Ход обработки объектов очень динамичен и быстро развивается. Исследования процесса категоризации одушевленности объектов, которые используют метод оценки вызванных потенциалов, анализируют соотношения амплитуд N100-P200; P(N)300; N400 [3; 17].
Процесс перестройки нейронных сетей при шизофрении по сравнению с группой здоровых людей при категоризации объектов живой и неживой природы остается до конца не изученным [5; 6; 30].
В недавнем исследовании категоризации объектов живой и неживой природы у людей с умеренными когнитивными расстройствами (MCI) Karimi и коллеги, рассматривали задачу зрительной категоризации одушевленности объектов как более сложную, чем типичные задачи на память, что делает её более чувствительной к тонким изменениям нейронных процессов у людей из ненормативных выборок. Методом вызванных потенциалов было выявлено снижение амплитуды P300 [19; 25].
Также было показано, что существует связь между изменением восприятия и интеграционных процессов у людей с шизофренией и изменениями в восприятии зрительных стимулов с определёнными пространственными и временны́ми характеристиками, работой определённых нейронных систем (низкочастотной — магно-системой и высокочастотной — парвосистемой) [4; 5; 24].
Для оценки когнитивных изменений у людей, страдающих шизофренией, а также людей, находящихся в группе риска, применяется метод когнитивных зрительных вызванных потенциалов в ответ на определенную задачу [2; 17; 24; 27]. В качестве маркеров шизофрении выделяют аномалии в амплитудах ряда компонентов: P50, N100, MMN, P300, N 400, P500 [5; 11; 21; 29; 32].
Целью данного исследования была оценка особенностей активности мозга людей, страдающих шизофренией, при восприятии и категоризации объектов живой и неживой природы, имеющих различные пространственно-частотные характеристики.
На основе приведённых выше данных об изменениях амплитуд вызванных потенциалов предполагалось, что паттерны мозговой активности на ранних и поздних этапах зрительной обработки при категоризации объектов живой и неживой природы различаются у людей, страдающих шизофренией, и людей из нормативной выборки.
МЕТОДИКА
В исследовании на основе добровольного информированного согласия приняли участие 25 людей с параноидной формой шизофрении легкой и средней степени тяжести (F20 по МКБ – 10): 17 мужчин и 8 женщин в возрасте от 20 до 35 лет с продолжительностью болезни от 1 до 7 лет без офтальмологической патологии. Данные 7 человек не были включены в выборку из-за невозможности выделения компонентов вызванных потенциалов в силу сильной зашумленности записи ЭЭГ. Все участники исследования находились в стационаре и получали терапию атипичными антипсихотиками (арипипразол). Условия проведения исследований соответствовали этическим нормам Хельсинкской декларации всемирной медицинской ассоциации. Все участники исследования подписывали информированное согласие.
Среди симптомов, которые наблюдались у людей с шизофренией, участвовавших в исследовании, необходимо отметить эмоциональную однообразность, гипомимичность, напряженность, настороженность, тревожность. Были характерны также слуховые галлюцинации (голоса). Для них было характерно доминирование продуктивных симптомов над негативными. Наблюдались нарушения структурирования мышления, снижение способности к концентрации внимания и сосредоточению, но не было выявлено нарушений поведения.
Функциональные изменения зрительной системы анализировались с помощью метода когнитивных зрительных вызванных потенциалов, описанного ранее [3; 5]. Участник исследования располагался в затемненной комнате без посторонних раздражителей перед экраном монитора (17 дюймов) на расстоянии 1 м. Предъявлялись изображения объектов, подвергнутые цифровой фильтрации путем свертки изображений с DoG-функцией (сокр. от Difference Of Gaussians), представляющей собой разность двух двумерных функций Гаусса с различной полушириной. Параметры фильтров были подобраны так, чтобы изображения объектов вызывали избирательную активацию двух систем зрения: высокочастотной парво-системы (с максимальным значением пропускания на частоте 10 цикл/град) и низкочастотной магно-системы (на частоте 1 цикл/град). Был использован набор из 90 монохромных контурных изображений в оттенках серого цвета — половина изображений живой природы, половина — неживой природы (рис. 1). Каждая сессия состояла из 360 предъявлений, 45 изображений объектов каждой из четырёх категорий (живое/неживое в виде изображения с высоким/низким значением пропускания) предъявлялись в случайном порядке дважды на экране монитора. Средняя яркость и контраст всех изображений были одинаковы. Интервал между предъявлениями — 1700 мс, длительность предъявления изображения объекта — 170 мс, помимо этого было предусмотрено время (500 мс) для нажатия участником исследования на кнопку при решении задачи.
Требовалось максимально быстрое нажатие человеком на одну клавишу мыши, когда он видит объект живой природы, и на другую клавишу, когда на экране предъявлен объект неживой природы. Половина людей в ответ на предъявление объекта живой природы нажимала левую клавишу мыши, а другая половина — правую клавишу (в случайном порядке). В записи регистрировались метки проб на момент предъявления объекта на экране, независимо от того, когда человек нажимал на кнопку.
Рис. 1. Пример черно-белого изображения – объекта неживой природы, подвергнутого цифровой фильтрации путем свертки с DoG-функцией в области высоких (а) и низких пространственных частот (б).
Вызванные потенциалы регистрировались с помощью энцефалографа “Мицар-ЭЭГ-202” и программы WinEEG с помощью шапочки Electrocap с 19-ю электродами, расположенными на поверхности головы по системе 10–20 в отведениях Fp1; Fp2; F7; F3; Fz; F4; F8; T3; C3; Cz; C4 T4; T5; P3; Pz; P4; T6; O1; O2. Референтные электроды располагались на мочках ушей, а заземляющий электрод — в лобной области. Частота дискретизации составляла 250 Гц, полоса пропускания усилителей — 0.32–35 Гц.
Для обработки записи ЭЭГ использовался метод, описанный ранее [3; 5]. Коррекцию артефактов морганий глаз провели с помощью метода независимых компонентов [2; 3; 7]. После автоматического метода фильтрации независимых компонентов проводилось ручное удаление артефактов. Участок выделялся и вырезался, при дальнейшем усреднении эти участки не учитывались. Коррекция по базовой линии осуществлялась автоматически, задаваясь в программе WinEEG. Изолиния составила 300 мс до начала предъявления изображения объекта. Эпоха анализа продолжительностью в 700 мс была разделена на временные интервалы, соответствующие компонентам: N60, P100 (N100), N170 (P170), N200, N250 (P250), P300, P500. Для каждой области мозга выбирался более точный временной интервал [9]. В каждом временно́м окне находили значения амплитуды, соответствующие пикам основных компонентов вызванного потенциала (максимум для позитивных волн и минимум для негативных волн) для каждого отведения (табл. 1). С помощью программы WinEEG было проведено усреднение 90 эпох вызванных потенциалов для каждого из 4 типов объектов по отдельности.
Статистический анализ данных проводился с использованием двухфакторного дисперсионного анализа ANOVA с зависимыми переменными — амплитудами вызванных потенциалов и факторами — частота (высокие/низкие частоты) и вид объекта (живые/неживые объекты природы) с последующими апостериорными множественными сравнениями по Бонферрони. Статистические решения принимались на 5%-ом уровне значимости, данные представлены средними и стандартными отклонениями Mean± SD (на графике представлены средние с ошибками средних SE). Расчеты проводились с использованием программного комплекса в программе SPSS Inc 13 [1].
Таблица 1. Временные интервалы, соответствующие компонентам зрительных вызванных потенциалов, для различных отведений
| Отведение | Компонент | Начальная граница периода, мс | Конечная граница периода, мс | |
| Cz | N | 100 | 136 | 156 |
| Cz | P | 170 | 160 | 248 |
| Cz | N | 250 | 252 | 320 |
| Cz | P | 300 | 324 | 464 |
| Cz | P | 500 | 468 | 696 |
| T5, T6 | N | 60 | 72 | 100 |
| T5, T6 | P | 100 | 104 | 180 |
| T5, T6 | N | 200 | 184 | 220 |
| T5, T6 | P | 250 | 224 | 320 |
| Pz | P | 170 | 216 | 332 |
| Pz | N | 250 | 336 | 380 |
| Pz | P | 300 | 384 | 428 |
| Pz | P | 500 | 432 | 700 |
| O1, O2 | N | 60 | 92 | 120 |
| O1, O2 | P | 100 | 120 | 180 |
| O1, O2 | N | 170 | 184 | 216 |
| O1, O2 | P | 250 | 220 | 384 |
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ
В ходе статистической обработки данных были выделены компоненты зрительных вызванных потенциалов, по которым выявлены значимые различия амплитуды в зависимости от факторов: частота изображения, вид объекта, и их взаимодействия (таб. 2).
Таблица 2. Значимости главных эффектов p ANOVA, df1=1, df2=24 (значимые эффекты при p<0.05 выделены жирным шрифтом) по отведениям для компонентов вызванных потенциалов
| Отведение | Компонент | Время | Частота изображения (ВЧ-НЧ) | Вид объекта (Жив-Нежив) | Взаимодействие факторов |
| O1 | N | 60 | 0.020 | 0.677 | 0.242 |
| O2 | N | 60 | 0.030 | 0.379 | 0.709 |
| T5 | N | 60 | 0.184 | 0.550 | 0.042 |
| T6 | N | 60 | 0.384 | 0.579 | 0.591 |
| Cz | N | 100 | 0.333 | 0.507 | 0.701 |
| O1 | P | 100 | 0.000 | 0.982 | 0.193 |
| O2 | P | 100 | 0.000 | 0.844 | 0.031 |
| T5 | P | 100 | 0.003 | 0.441 | 0.758 |
| T6 | P | 100 | 0.181 | 0.889 | 0.181 |
| Cz | P | 170 | 0.005 | 0.265 | 0.572 |
| O1 | N | 170 | 0.017 | 0.794 | 0.212 |
| O2 | N | 170 | 0.003 | 0.373 | 0.713 |
| Pz | P | 170 | 0.059 | 0.007 | 0.686 |
| T5 | N | 200 | 0.184 | 0.949 | 0.027 |
| T6 | N | 200 | 0.862 | 0.442 | 0.740 |
| Cz | N | 250 | 0.916 | 0.01 | 0.044 |
| O1 | P | 250 | 0.395 | 0.004 | 0.295 |
| O2 | P | 250 | 0.386 | 0.023 | 0.393 |
| Pz | N | 250 | 0.828 | 0.003 | 0.053 |
| T5 | P | 250 | 0.002 | 0.006 | 0.972 |
| T6 | P | 250 | 0.010 | 0.001 | 0.926 |
| Cz | P | 300 | 0.181 | 0.051 | 0.95 |
| Pz | P | 300 | 0.158 | 0.006 | 0.463 |
| Cz | P | 500 | 0.258 | 0.392 | 0.335 |
| Pz | P | 500 | 0.000 | 0.243 | 0.851 |
Результаты сравнений амплитуд компонентов показывают, что на ранних этапах обработки зрительной информации уже начиная с 60 мс значимо отличаются амплитуды волн при изменении пространственно-частотных характеристик изображений. Наблюдается достоверные отличия амплитуд в затылочных отведениях (O1 и О2) для компонентов N60, P100, N170 и височных отведениях (левая сторона T5) для P100 и P250, в центральном вертексном отведении (Cz) для компонента P170, в теменном отведении (Pz) для компонента P170 (на уровне тенденции) и P500, в задневисочном отведении (правая сторона: T6) для компонента P250. Начиная с 170 мс зафиксировано значимое различие амплитуд в зависимости от изменения семантики объекта (объект живой/неживой природы) в центрально-теменном отведении (Pz). Различие амплитуд компонента P250 (N250) в зависимости от изменения семантики объекта зафиксировано во всех исследованных зонах коры головного мозга: затылочных, задневисочных, центрально-теменном и центральном вертексном отведении.
Амплитуды компонентов P100 и N170 в затылочных отведениях, P100 в задневисочных и P170 в центрально-теменном отведении были достоверно выше при категоризации объектов, изображённых с помощью низких пространственных частот, чем при категоризации объектов, изображённых с помощью высоких пространственных частот. В центрально-теменном и центральном (вертекс) отведении достоверного различия для компонентов P100, N170, P300 и P500 при категоризации объектов, изображенных, преимущественно на основе низких и высоких пространственных частот, выявлено не было. От категории объекта этот эффект не зависел. А в правом задневисочном отведении амплитуда компонента P100 и в центрально-теменном отведении амплитуда компонента P170 на низких пространственных частотах были достоверно выше, чем на высоких только при категоризации объектов неживой природы.
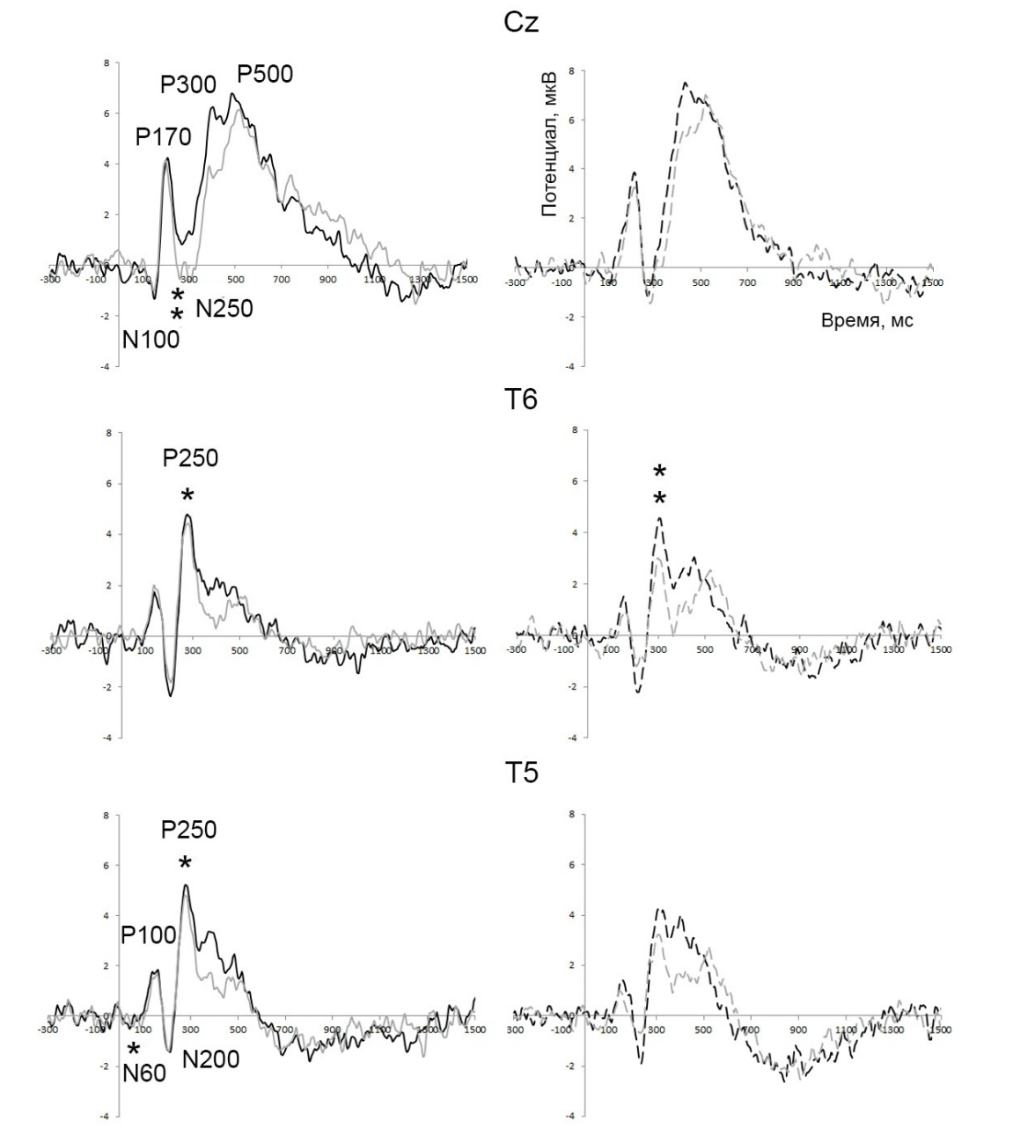
Было обнаружено значимое различие амплитуд компонентов при категоризации объектов живой и неживой природы, изображённых на основе низких пространственных частот: для компонента N60 — в левом задневисочном отведении (T5) (рис. 2), для компонента N250 — в центральном (вертекс) отведении (Cz), для компонента P250 — в правом затылочном (O2) и левом задневисочном отведениях (T5). Достоверное различие амплитуд при категоризации объектов живой и неживой природы при их изображении с помощью высоких пространственных частот было получено: для компонента P100 — в правом затылочном отведении (O2), для компонента N250 — в центрально-теменном отведении (Pz), для компонента P250 — в левом затылочном отведении (O1) (таб. 3).
Амплитуда всех вышеперечисленных компонентов в ответ на изображения живой природы были достоверно выше амплитуды компонентов, возникающих в ответ на изображения неживой природы. В центральном (вертекс) отведении для компонентов P100 (N100), N170 (P170), P300 и P500; в правом задневисочном отведении для компонентов N60, P100 (N100); в затылочных отведениях N60, P100 (N100); в левом затылочном отведении N170 (P170); в задневисочных отведениях N200; в центральном теменном отведении для компонента P500 достоверного отличия выявлено не было (рис. 3). В задневисочных и затылочных отведениях компонент P300 невозможно было выделить из-за сильной зашумлённости зарегистрированной электрической активности.
Таблица 3. Усредненные значения амплитуд компонентов вызванных потенциалов по отведениям в зависимости от вида объекта (мкВ), где Ж — объекты живой природы, НЖ — объекты неживой природы. Значимости главных эффектов p ANOVA, df1=1, df2=24 (p<0.05) для объектов разной семантики (живой и неживой природы), изображенных с помощью низких и высоких пространственных частот.
| Отведение | Компонент | При высоких частотах | При низких частотах | ||||
| Ж | НЖ | p Anova | Ж | НЖ | p Anova | ||
| Cz | N100 | -1.27 | -1.10 | - | -1.05 | -0.52 | - |
| P170 | 3.53 | 2.85 | - | 4.82 | 4.64 | - | |
| N250 | -1.99 | -1.96 | - | -0.96 | -2.82 | 0.007** | |
| P300 | 5.56 | 4.72 | - | 4.91 | 4.11 | - | |
| P500 | 8.06 | 8.07 | - | 7.92 | 7.11 | - | |
| T5 | N60 | -0.99 | -1.45 | - | -1.19 | -0.40 | 0.018* |
| P100 | 2.83 | 2.67 | - | 4.37 | 4.03 | - | |
| N200 | -0.93 | -1.50 | - | -0.71 | -0.19 | - | |
| P250 | 7.17 | 6.37 | - | 8.40 | 7.62 | 0.026* | |
| T6 | N60 | -1.25 | -1.22 | 0.024* | -0.82 | -1.17 | 0.064 |
| P100 | 3.25 | 2.79 | - | 3.29 | 3.84 | - | |
| N200 | -1.37 | -1.22 | - | -1.41 | -1.01 | - | |
| P250 | 6.94 | 5.63 | - | 7.96 | 6.71 | - | |
| Pz | P170 | 7.80 | 6.53 | 0.005** | 8.50 | 7.52 | 0.011* |
| N250 | 2.80 | 0.83 | 0.001** | 2.19 | 1.62 | - | |
| P300 | 6.54 | 4.82 | 0.018* | 5.66 | 4.44 | 0.021* | |
| P500 | 7.96 | 7.40 | - | 6.25 | 5.86 | - | |
| O1 | N60 | -1.56 | -2.05 | - | -0.87 | -0.57 | - |
| P100 | 2.37 | 1.77 | - | 5.20 | 5.79 | - | |
| N170 | -1.92 | -2.35 | - | -0.27 | 0.38 | - | |
| P250 | 9.52 | 8.00 | 0.003** | 9.57 | 8.78 | - | |
| O2 | N60 | -1.58 | -1.90 | - | -0.60 | -0.72 | - |
| P100 | 3.11 | 2.15 | 0.017* | 5.54 | 6.65 | - | |
| N170 | -1.84 | -1.67 | - | 0.54 | 1.01 | - | |
| P250 | 10.66 | 9.88 | - | 11.35 | 10.07 | 0.025* |
Примечание. Ж — объекты живой природы; НЖ — объекты неживой природы. Звездочками показаны достоверные различия в зависимости от уровня значимости при сравнении соотношения амплитуд одного компонента внутри каждой группы. Уровень значимости: * — p
А Б
Рис. 2. Усредненные вызванные потенциалы, зарегистрированные у людей с шизофренией в центральном отведении (Сz), в затылочно-височном отведении слева (T5) и справа (Т6) при категоризации изображений объектов живой (чёрная линия) и неживой (серая линия) природы, отфильтрованные по низким (А) и по высоким пространственным частотам (Б). Звездочками показаны достоверные различия в зависимости от уровня значимости при сравнении соотношения амплитуд одного компонента внутри каждой группы по низким и высоким пространственным частотам. Уровень значимости: * — p
ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ РЕЗУЛЬТАТОВ
Ранее в исследованиях категоризации у людей без патологии с использованием регистрации позитронно-эмиссионной томографии (ПЭТ), МЭГ, ЭЭГ и ФМРТ было показано, что при распознавании одушевленных и неодушевленных объектов активируются разные структуры головного мозга [13; 15; 16; 18]. В исследованиях патологии психики обнаружены случаи избирательного ухудшения распознавания одушевленных или неодушевленных объектов, например, при болезни Альцгеймера [19].
Предварительные данные, полученные нами на небольшой группе людей с шизофренией, показали, что при категоризации объектов живой и неживой природы вероятность правильных ответов у людей с шизофренией соответствует данным контрольной нормативной группы [5]. В настоящем исследовании люди, страдающие шизофренией, принимали атипичный антипсихотик арипипразол, однако необходимо отметить, что в недавней масштабной работе, где изучалось влияние различных антипсихотиков на ЭЭГ человека, у группы пациентов, которая принимала арипипразол, не выявили значимых отличий в спектральной активности в сравнении с контрольной группой, не принимавшей антипсихотики [28].
При анализе записи ЭЭГ людей с шизофренией в настоящем исследовании было выявлено, что для объектов живой и неживой природы различается амплитуда компонента N60 в левом задневисочном отведении при низкой пространственной частоте изображения, что может указывать на начало процесса различения данных объектов. Это сопоставимо с данными, полученными другими исследователями на нормативной выборке: предъявление объектов живой и неживой природы характеризуется вызванными потенциалами, различия между которыми начинают возникать через 80 ± 20 мс после появления объекта и достигают своего пика в течение 250 ± 50 мс. Данный эффект характерен для задневисочных, центральных и теменных областей головного мозга [13]. В проведенном нами исследовании амплитуда потенциалов, возникавших при предъявлении объектов живой природы, превышала амплитуду потенциалов, возникавших на объекты неживой природы в затылочных, левом задневисочном и центральных отведениях в зависимости от пространственных частот изображения. При низкой частоте изображения это было характерно для компонента N60 влевом задневисочном отведении (T5) (рис. 2), для компонента N250 в центральном отведении (Cz), для компонента P250 в правом затылочном (O2) и левом задневисочном отведениях (T5). Достоверное различие амплитуд вызванных потенциалов на объекты живой и неживой природы, изображенные на основе высоких пространственных частот, было получено для компонента P100 — в правом затылочном отведении (O2), для компонента N250 — в центрально-теменном отведении (Pz), для компонента P250 — в левом затылочном отведении (O1).
Данные, полученные на группе людей без патологии, выполнявших подобную экспериментальную задачу, показали, что при категоризации объектов живой и неживой природы в интервале времени 150–220 мс амплитуда N170 в правом и левом задневисочных отведениях, P/N250 и P300 для всей зоны интереса зависит от категории объектов [3].
Нами получены данные об отсутствии у людей с шизофренией достоверных различий амплитуд ранних компонентов в интервалы времени 150–220 в левом и правом задневисочных и центральном отведениях при предъявлении объектов живой и неживой природы. Эти результаты можно косвенно сравнить с данными, полученными Maher и коллегами при исследовании аналогичной группы участников исследования: было показано отсутствие различия в амплитуде P170 (N170) в правом задневисочном отведении на стимулы, содержащие лица, по сравнению с амплитудой того же компонента на изображения неодушевленных объектов (деревья), тогда как у людей без патологии это различие было зафиксировано для всех видов объектов, представленных разными уровнями контрастности [23; 31].
В настоящем исследовании также было обнаружено, что у людей с шизофренией компонент P300 достоверно не отличается по амплитуде в центральном отведении при предъявлении объектов живой и неживой природы. В ряде исследований было показано, что амплитуда P300 пропорциональна ресурсам внимания, выделенным для данной задачи [8; 22]. Можно предположить, что отсутствие значимого увеличения P300 на объекты живой природы по сравнению с объектами неживой природы у людей с шизофренией, отражает меньшее распределение ресурсов внимания на объекты живой природы по сравнению с нормативной выборкой. Исследования Oribe и коллег продемонстрировали прогрессирующее снижение амплитуды Р300 в ответ на визуальные стимулы на ранней стадии шизофрении (в течение первого года после возникновения у людей с шизофренией первого эпизода) [26].
Оценка взаимодействия семантических и физических характеристик предъявляемых объектов и их связи с работой зрительной системы позволила выявить компоненты и зоны, на которые влияют оба вида характеристик. В левом задневисочном отведении амплитуды ряда компонентов (N60, N200) и левом затылочном отведении (N60) на изображения низкой частоты ниже амплитуды компонентов, возникающих на изображения высокой пространственной частоты, только для объектов неживой природы. А для объектов живой природы этот эффект не выявлен.
По полученным нами данным, вне зависимости от одушевленности объекта, имеет место достоверное различие амплитуд потенциалов, возникающих при предъявлении объектов, изображенных на основе высоких и низких пространственных частот: в затылочных, задневисочных и центральных отведениях для компонентов P100, и P170 (N170) P100 —– амплитуда потенциалов на предъявление изображений низкой пространственной частоты была выше, чем на предъявление изображений высокой пространственной частоты. Амплитуды также достоверно не различались для компонентов P100, N170, P300 и P500, т.е. не зависели от вида объекта. В отдельных отведениях (правом задневисочном и центрально-теменном) амплитуда вызванных потенциалов была выше на объекты неживой природы, по сравнению с объектами живой природы.
В ходе наших ранних исследований у нормативной выборки было выявлено другое соотношение амплитуд вызванных потенциалов. В затылочных, задневисочных, теменных и центральных отведениях амплитуды компонентов P100, P170 (N170), N250(P250), P300 и P500 были достоверно ниже при предъявлении изображений низкой пространственной частоты по сравнению с изображениями высокой пространственной частоты вне зависимости от категории объекта [5]. Как отмечается, обработка высокочастотных изображений связана с парво-системой. Эта система по результатам исследований у новорожденных формируется позже [33] и может быть развита благодаря дополнительному зрительному опыту [12].
Итак, с помощью электрофизиологического метода категоризации одушевлённости у людей, страдающих шизофренией от 1 года до 7 лет, были получены данные, указывающие на изменения паттернов их мозговой активности при распознавании объектов живой и неживой природы, которые могут свидетельствовать о преимущественном снижении у них активности парво-системы (системы объектного зрения).
Выявленный результат важен для лучшего понимания перестройки нейронных сетей при зрительном восприятии объектов разных категорий, возникающих при развитии шизофрении.
В ходе исследования было проведено усреднение 90 эпох вызванных потенциалов для каждого вида объектов по отдельности. Этого количества было достаточно для получения статистически значимых различий, что подтверждается результатами более ранних наших работ [3; 5], где были получены различия от ранних (Р100 и N100) до поздних вызванных потенциалов (Р300–Р500). В дальнейшем представляется целесообразным увеличение числа эпох для подтверждения полученных результатов на большей выборке.
ВЫВОДЫ
У людей, страдающих шизофренией, выявлены паттерны мозговой активности, отражающие репрезентации объектов живой и неживой природы, отличные от таковых паттернов у ранее обследованных людей без патологии.
- У людей, страдающих шизофренией, не выявлено достоверных различий амплитуд вызванных потенциалов в интервале времени 150–220 мс в левом и правом задневисочных и центральном отведениях при предъявлении объектов живой и неживой природы, которые обнаруживаются у людей из нормативной выборки.
- У людей, страдающих шизофренией, не обнаружено достоверных различий в амплитуде P300 в центральном отведении при предъявлении объектов живой и неживой природы, которые характерны для мозговой активности людей без патологии.
- У людей, страдающих шизофренией, при предъявлении им объектов живой природы возникали вызванные потенциалы, амплитуды которых в затылочных, задневисочных и центральных отведениях превышали амплитуды вызванных потенциалов при предъявлении объектов неживой природы.
Библиография
- 1. Вершинина Е.А., Сафарова Г.Л. О применении методов математической статистики в клинических и экспериментальных исследованиях // Успехи геронтологии. 2019. Т. 32. № 6. С. 1052–1062.
- 2. Кропотов Ю.Д., Пронина М.В., Поляков Ю.И., Пономарев В.А. Функциональные биомаркеры в диагностике психических заболеваний: когнитивные вызванные потенциалы // Физиология человека. 2013. Т. 39. № 1. С. 14–25.
- 3. Моисеенко Г.А., и др. Классификация и распознавание изображений живой и неживой природы // Оптический журнал. 2015. Т. 82. № 10. С. 53–64.
- 4. Муравьева С.В., и др. Стимуляция работы зрительной системы с помощью когнитивной задачи в условиях виртуальной среды у пациентов с шизофренией и депрессией // Физиология человека. 2020. Т. 46. № 5. С. 27–36.
- 5. Муравьева С.В., и др. Исследование зрительных когнитивных вызванных потенциалов при шизофрении на ранних стадиях заболевания и их коррекция при помощи интерактивных виртуальных сред // Физиология человека. 2017. Т. 43. № 6. С. 24–36.
- 6. Шелепин Ю.Е., и др. Методы иконики и методы картирования мозга в оценке функционального состояния зрительной системы // Сенсорные системы. 2014. Т. 28. № 2. С. 61–75.
- 7. Щемелева О.В., и др. Электрофизиологические показатели деятельности мозга в процессе вербального и невербального взаимодействия собеседников // Физиология человека. 2019. T. 45. № 6. C. 16–26.
- 8. Abhishek P., et al. Lower P300 amplitudes for internally-generated events in patients with schizophrenia // Asian Journal of Psychiatry. 2018. V. 35. P. 67–71.
- 9. Andrade G.N., et al. Atypical visual and somatosensory adaptation in schizophrenia-spectrum disorders // Translational Psychiatry. 2016. V. 6. (5). № e804.
- 10. Behroozi M., Daliri M.R., Shekarchi B. EEG phase patterns reflect the representation of semantic categories of objects // Medical & biological engineering & computing. 2016. V. 54. № 1. P. 205–221.
- 11. Bodatsch M., Brockhaus-Dumke A., Klosterkötter J., Ruhrmann S. Forecasting psychosis by event-related potentials—systematic review and specific meta-analysis // Biological psychiatry. 2015. V. 77. № 11. P. 951–958.
- 12. Bosworth R.G., Dobkins K.R. Effects of prematurity on the development of contrast sensitivity: testing the visual experience hypothesis // Vision Research. 2013. V. 82. P. 31–41.
- 13. Carlson T., Tovar D.A., Alink A., Kriegeskorte N. Representational dynamics of object vision: The first 1000 ms // Journal of vision. 2013. V. 13 № 10. P. 1. doi: https://doi.org/10.1167/13.10.1.
- 14. Cerino R., Vergara S. How objects categorize the human brain: EEG and fMRI as analysis point // Res. Comput. Sci. 2020. V. 149. № 4. P. 43–55.
- 15. Clarke A., Devereux B.J., Randall B., Tyler L.K. Predicting the time course of individual objects with MEG // Cerebral Cortex. 2015. V. 25. № 10. P. 3602–3612.
- 16. Contini E.W., Wardle S.G., Carlson T.A. Decoding the time-course of object recognition in the human brain: From visual features to categorical decisions // Neuropsychologia. 2017. V. 105. P. 165–176.
- 17. Devia C., et al. EEG classification during scene free-viewing for schizophrenia detection // IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering. 2019. V. 27. № 6. P. 1193–1199.
- 18. Grootswagers T., Robinson A.K., Shatek S.M., Carlson T.A. Untangling featural and conceptual object representations // NeuroImage. 2019. V. 202:116083.
- 19. Karimi H., et al. Temporal dynamics of animacy categorization in the brain of patients with mild cognitive impairment // PloS One. 2022. V. 17. № 2. P. e0264058.
- 20. Khaligh-Razavi S.M., Cichy R.M., Pantazis D., Oliva A. Tracking the spatiotemporal neural dynamics of real-world object size and animacy in the human brain // Journ. of Cognitive Neuroscience. 2018. V. 30. № 11. P. 1559–1576.
- 21. Kiang M., Gerritsen C.J. The N400 event-related brain potential response: A window on deficits in predicting meaning in schizophrenia // International Journ. of Psychophysiology. 2019. V. 145. P. 65–69.
- 22. Li F., et al. The Time-Varying Networks in P300:_newline A Task-Evoked EEG Study // IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering. 2016. V. 24. № 7. P. 725–733.
- 23. Maher S., et al. Deficient cortical face-sensitive N170 responses and basic visual processing in schizophrenia // Schizophr. Res. 2016. V. 170. № 1. P. 87–94.
- 24. Martínez A., et al. Neural oscillatory deficits in schizophrenia predict behavioral and neurocognitive impairments // Frontiers in Human Neuroscience. 2015. V. 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2015.00371
- 25. Mudar R.A., et al. The effects of amnestic mild cognitive impairment on Go/No Go semantic categorization task performance and event-related potentials // Journal of Alzheimer's Disease. 2016. V. 50. № 2. P. 577–590.
- 26. Oribe N., et al. Progressive reduction of visual P300 amplitude in patients with first-episode schizophrenia: an ERP study // Schizophrenia bulletin. 2015. V. 41. № 2. P. 460–470.
- 27. Oribe N., et al. Early and late stages of visual processing in individuals in prodromal state and first episode schizophrenia: An ERP study // Schizophrenia Research. 2013. V. 146. P. 95–102.
- 28. Ozaki T, Toyomaki A, Hashimoto N, Kusumi I. Quantitative resting state electroencephalography in patients with schizophrenia spectrum disorders treated with strict monotherapy using atypical antipsychotics // Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2021. V. 19. № 2. P. 313–322.
- 29. Perrottelli A., et al. EEG-based measures in at-risk mental state and early stages of schizophrenia: a systematic review // Frontiers in Psychiatry. 2021. V. 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2021.653642
- 30. Pokorny V.J., et al. Aberrant cortical connectivity during ambiguous object recognition is associated with schizophrenia // Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging. 2021. V. 6. № 12. P. 1193–1201.
- 31. Salisbury D.F., et al. Neutral face and complex object neurophysiological processing deficits in long-term schizophrenia and in first hospitalized schizophrenia-spectrum individuals // International Journal of Psychophysiology. 2019. № 145. P. 57–64.
- 32. Sklar A.L., Coffman B.A., Salisbury D.F. Localization of early-stage visual processing deficits at schizophrenia spectrum illness onset using magnetoencephalography // Schizophrenia Bulletin. 2020. V. 46. №. 4. P. 955–963.
- 33. Tremblay E., et al. Delayed early primary visual pathway development in premature infants: high density electrophysiological evidence // PLoS One. 2014. V. 9 № 9. e107992.
- 34. Vaziri-Pashkam M., Taylor J., Xu Y. Spatial frequency tolerant visual object representations in the human ventral and dorsal visual processing pathways // Journ. of Cognitive Neuroscience. 2019. V. 31. № 1. P. 49–63.